Facteurs de risque
Facteurs de risque
Les principaux facteurs de risque du cancer de la prostate pour un homme
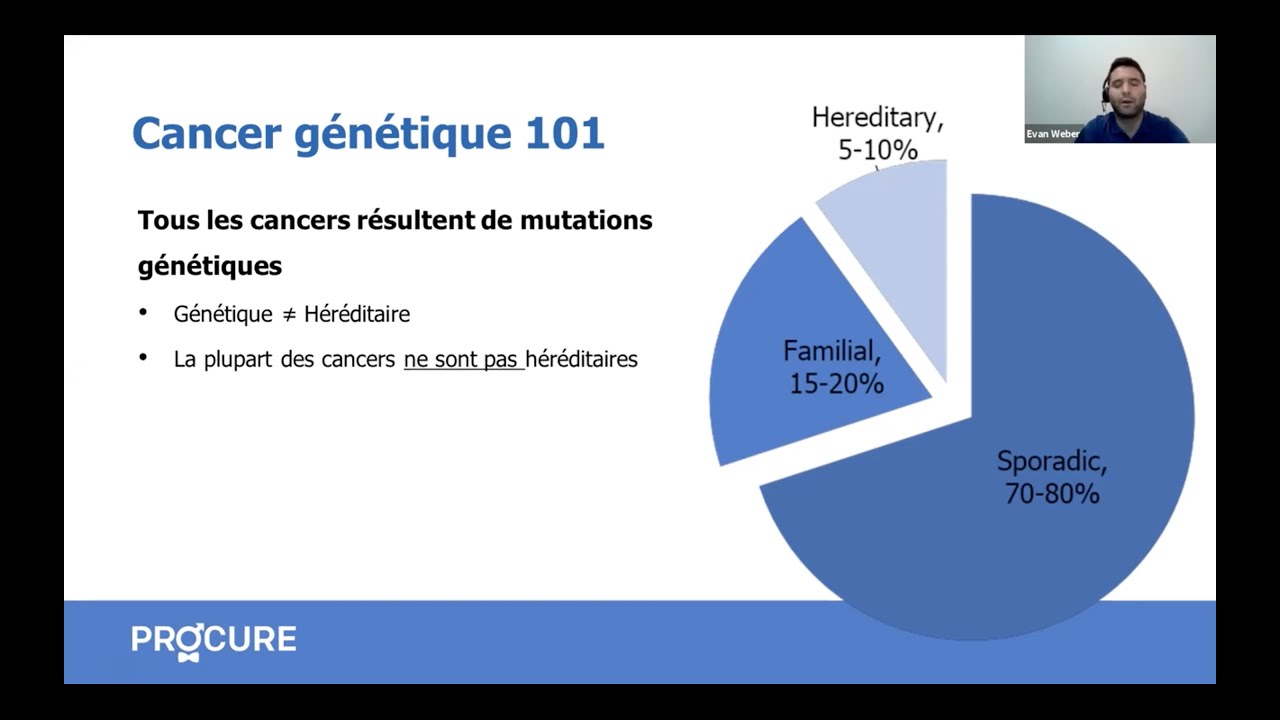
Les principaux facteurs de risque établis pour le cancer de la prostate sont l’âge, les risques étant plus élevés après 50 ans, l’histoire familiale de cancer et l’origine ethnique noire. Il est évident que ces facteurs ne peuvent pas être modifiés. Mais qu’en est-il de la prévention? Peut-on réduire le risque de développer un cancer de la prostate?
En explorant les pages de cette section, vous pourrez évaluer si vous présentez un risque plus élevé que d’autres hommes de développer un cancer de la prostate et peut-être prendre la décision d’adopter un mode de vie qui pourrait réduire vos risques ou améliorer votre qualité de vie.
Si vous avez des questions ou des préoccupations, n’hésitez pas à nous contacter au 1 855 899-2872 ou via le clavardage pour discuter avec l’un de nos professionnels de la santé spécialisés en uro-oncologie.
Informations pertinentes et complémentaires
Retrouvez ici une sélection de pages et de ressources clés pouvant répondre à vos questions ou préoccupations. Faites défiler pour explorer les informations essentielles disponibles sur notre site.

Votre pénis est courbé?

Puis-je prévenir un cancer de la prostate lié au BRCA?

Le cancer de la prostate est-il héréditaire?
Génétique et cancer de la prostate

Symptômes, risque et dépistage

De la prostate au dépistage