Your prostate
- Prostate cancer
- Your prostate
- Anatomy
- Structure
- Function

Your prostate
A sexual gland exclusive to men
The role of the prostate is essential for fertility. During childhood, the prostate is very small. It begins to grow during puberty when testosterone, a male sex hormone, increases, leading to the growth of the penis, testicles, and scrotum. It is during this period that it becomes one of the male reproductive organs, as it secretes nutrients and fluid necessary for the survival of sperm. Without the prostate, there is no ejaculation. Therefore, the role of the prostate is primarily “useful” for reproduction.
Your prostate also secretes a protein called prostate-specific antigen, or PSA, which keeps sperm in liquid form after ejaculation. This protein is found in small amounts in the blood and provides indications of prostate health. It is an integral part of screening, diagnosis, and follow-up after treatment.
Learn more about its anatomy, structure, and function on this page. If you have any questions or concerns, feel free to contact us at 1-855-899-2873 or via chat to speak with one of our healthcare professionals specialized in uro-oncology.

What is the prostate
The prostate is a sexual gland:
- Located between the bladder and the penis, just in front of the rectum;
- Formed of 2 lobes that surround the urethra, a canal that runs through the center of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis, allowing urine and sperm to flow out of the body;
- About the size of a walnut, which increases in size in your forties;
- With a soft, spongy texture to the touch.
The prostate is made of:
- Gland cells that secrete liquids for ejaculation;
- Muscle cells that participate in the evacuation of your sperm during ejaculation;
- Fiber cells that maintain the structure of the gland.
Around the prostate, we find:
- The seminal vesicles, glands that produce sperm and that are located on either side of the prostate;
- The vas deferens, the tube that carries sperm from the testicle to the seminal vesicles;
- The nerve bundles that control your bladder and erectile function and that are located on either side of your prostate.

Three main zones of the prostate
Peripheral zonee
- The peripheral zone is the largest area of the prostate. It can easily be felt by the doctor during a digital rectal exam (DRE).
- Most prostate cancers start in the peripheral zone.
Transition zone
- This is the area located in the middle of the prostate, between the peripheral and central areas. It surrounds your urethra that runs through the prostate.
- With age, the transitional area increases in size until it becomes the largest portion of your prostate. This is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or enlarged prostate.
Central zone
- It is the part of the prostate that is farthest from the rectum. This is why prostate tumors located in this area can not be felt by the doctor during a digital rectal examination.
- If the doctor is in doubt, the following information will help decide if additional investigation is necessary:
- Your PSA level
- Your age and family history
- Your ethnic origin

In short
Your fertility and natural fertilization
- It produces … a prostatic fluid rich in enzymes, proteins and minerals that nourishes and protects your spermatozoa.
- It makes … a protein (APS) that is used to liquefy your sperm to facilitate the mobility of your spermatozoa.
- It allows … ejaculation by contracting.
- It promotes … fertility through its enzymes facilitating the penetration of sperm through the cervix.
- It is not related to the mechanism of erection. Therefore, the origin of erectile dysfunction lies elsewhere.
In more detail
The prostate is made up of thousands of tiny fluid-producing glands. Specifically, the prostate is an exocrine gland. Exocrine glands are so-called because they secrete through ducts to the outside of the body (or into a cavity that communicates with the outside). Sweat glands are another example of an exocrine gland.
The fluid that the prostate gland produces forms part of semen, the fluid that carries sperm during orgasm. This fluid, produced in the prostate, is stored with sperm in the seminal vesicles. When the male climaxes, muscular contractions cause the prostate to secrete this fluid into the urethra, where it is expelled from the body through the penis.
The prostate wraps itself around the urethra as it passes from the bladder to the penis. Prostatic changes can affect urine flow. Increasing the size of the prostate or muscle tone may impede the flow of urine due to the close anatomical relationship between the urethra and the prostate.
The prostate also produces a protein called prostate-specific antigen (PSA). PSA is released with the ejaculatory fluid and can also be traced in the bloodstream. The testing of PSA levels in the blood is used to detect prostate cancer. The level of PSA in the blood is usually measured in nanograms of PSA per milliliter of blood (ng/mL).
Usually, a PSA rate of less than 4 nanograms per milliliter of blood is normal, but age should also be taken into consideration as PSA levels gradually increase with age. A rise in PSA concentration may indicate the presence of:
- An enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia)
- An inflammation or infection of the prostate (prostatitis)
- A prostate cancer
Your doctor will have you undergo other tests to determine the exact cause of the increase in your PSA.
Additional Information - Your prostate

Is prostate cancer hereditary?
Understanding the hereditary and genetic aspects of this disease can provide valuable information to both individuals affected and their families.
Genetics and prostate cancer
Do you have a family history of cancer? Your doctor might recommend genetic screening.

Symptoms, risk and screening
Are you over 50 or experiencing urinary problems? Discover why early screening for prostate diseases is important.

From prostate to screening
Learn about the role of your prostate, related diseases, symptoms to watch out for and risk factors.
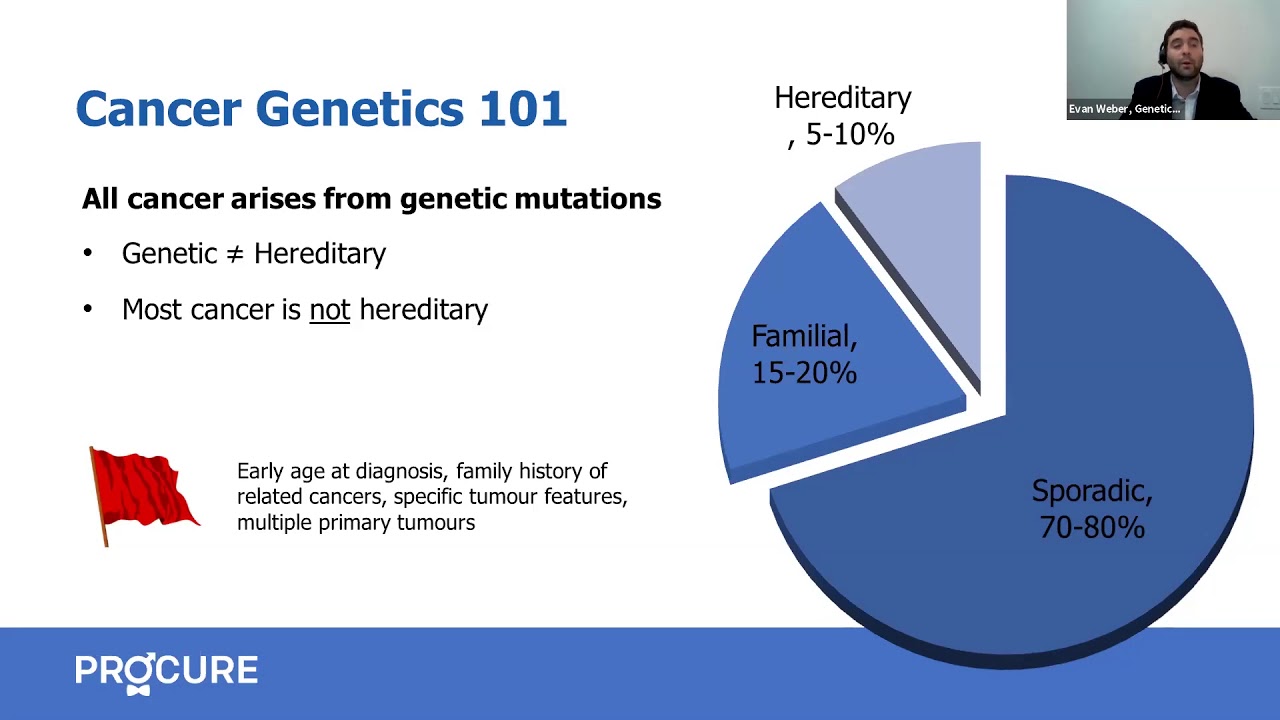
Genetic predisposition to prostate cancer
Although rare, some hereditary genetic mutations can increase your risk of prostate cancer.

Do you have a curved penis?
Is your penis curved? Does it curve to the left, right, upward, or downward? You have a curved penis and you or your partner want to know why?

Can I prevent BRCA-related prostate cancer?
How to prevent BRCA-related prostate cancer? Can I have a radical prostatectomy or a proactive treatment to prevent prostate cancer?

What is a genetic mutation?
Do you have a significant family history of cancer? Is there a link between prostate cancer and a genetic mutation?

My balls hurt!
While sore balls are a common experience and usually no cause for concern, it’s important to familiarise yourself with symptoms in case it’s a sign of something serious.

I feel a heaviness in my underwear
I feel a heaviness in my underwear and I know it’s not normal… And sure enough, you notice your balls are much bigger than usual.

What women should know about prostate cancer
As a woman, you might think that prostate cancer is not your concern because you don’t have a prostate. However, prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men.

Why a health check?
The short answer to this question is to assess your health. This is the starting point for a health check. Could we be in the presence of potential undetected diseases?

10 signs that encourage you to see a doctor
There are many reasons why men will be referred to a specialist, and if you experience any of the following symptoms you should see a family doctor. Here are 10 signs that encourage you to consult. You should also know that unless you go to a private clinic, you cannot consult a specialist directly, such as […]

From your prostate to screening in 5 points
From your prostate to screening in 5 points. Gentlemen, are you over 50 years old, or have you been having urinary problems for some time now? Several diseases can affect your prostate, and it’s important to detect them early. Let’s take a closer look. The size of a walnut, the prostate is located just below […]
Sources and references
Last medical and editorial review: April 2024. See our web page validation committee and our collaborators by clicking here.


